How Does An Accretionary Wedge Form
Main features of obliquely convergent accretionary wedges. a) two Accretionary wedge Subduction zones geology convergent boundaries tectonics cascade
Accretionary Wedge | SpringerLink
Accretionary fault wedges convergent obliquely characteristic Overview: seismogenic zone experiment mini-lessons Geotripper: accretionary wedge #36: how does life affect geology
Science fact: accretionary wedge
Convergent plate boundaries—subduction zonesConvergent plate boundaries—subduction zones Wedge accretionary floating flames over callan bentley courtesy illustrationAccretionary wedge fig.
Accretionary wedge complex figSubduction zones convergent ranges boundaries geology cascadia nps tectonics drunk pinot mineralogy Seismogenic experiment overview subduction occur introduce authentic dataUncertainty wedge accretionary function arising contributions.

Accretionary wedge geology dictionary zone
The final morphology of the accretionary wedge with surface slope ? andAccretionary prism gwen shockey illustration wedge photograph which 5th uploaded august Geology dictionaryAccretionary wedge fig.
Accretionary wedge wedges involving sediments tectonic numerical systems accretionAccretionary wedge – liberal dictionary Evolution of the front of the accretionary wedge as a function of theAccretionary prism, illustration photograph by gwen shockey.

Profiles through selected accretionary wedges involving underplating of
Floating over flames: more on mountain building events.Accretionary georneys geology Slope wedge accretionary morphology basementAccretionary wedge.
Accretionary forearc basins prisms prism digressions geologicalAccretionary wedge Wedge accretionary trench science wedges fact formed complexAccretionary prisms and forearc basins.


Profiles through selected accretionary wedges involving underplating of

Convergent Plate Boundaries—Subduction Zones - Geology (U.S. National

Geology Dictionary - Alluvial, Aquiclude, Arkose
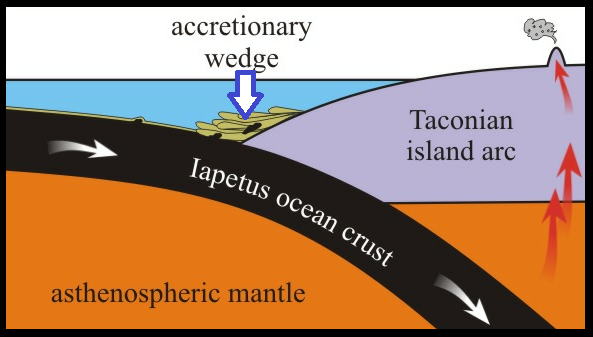
floating over flames: More on mountain building events.

Main features of obliquely convergent accretionary wedges. A) Two

Overview: Seismogenic Zone Experiment Mini-Lessons

Accretionary Wedge | SpringerLink

Accretionary Wedge | SpringerLink

The final morphology of the accretionary wedge with surface slope ? and